
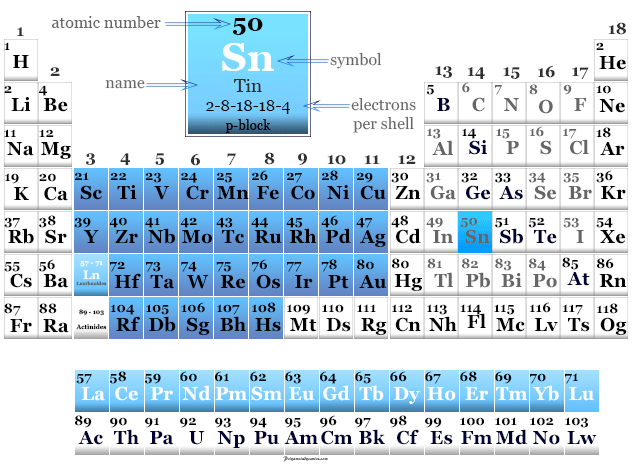
The crystal structure of tin is tetragonal. The melting point of tin is 231.9 C and its boiling point is 2602 C. The atomic mass of tin is 118.71 u and its density is 7.31 g/cm 3. When tin is polished, it produces a shiny surface. The above orbital diagram shows that the 1s subshell has 2 electrons, the 2s subshell has 2 electrons, the 2p subshell has 6 electrons, the 3s subshell has 2 electrons, the 3p subshell has 6 electrons, the 4s subshell has 2 electrons, the 3d subshell has 10 electrons, the 4p subshell has 6 electrons, the 5s subshell has 2 electrons, the 4d subshell has 10 electrons, and the 5p subshell has 2 electrons. Tin is a malleable metal and hence it can be drawn into thin sheets. The atomic number of each element increases by one, reading from left to right. Period A horizontal row in the periodic table.
#TIN PERIODIC TABLE HOW TO#
Learn how to draw: Tin Bohr Model #4 From its Orbital Diagram Members of a group typically have similar properties and electron configurations in their outer shell. So the electron configuration of tin will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 2.ġs 2 indicates that the 1s subshell has 2 electrons 2s 2 indicates that the 2s subshell has 2 electrons 2p 6 indicates that the 2p subshell has 6 electrons 3s 2 indicates that the 3s subshell has 2 electrons 3p 6 indicates that the 3p subshell has 6 electrons 4s 2 indicates that the 4s subshell has 2 electrons 3d 10 indicates that the 3d subshell has 10 electrons 4p 6 indicates that the 4p subshell has 6 electrons 5s 2 indicates that the 5s subshell has 2 electrons 4d 10 indicates that the 4d subshell has 10 electrons 5p 2 indicates that the 5p subshell has 2 electrons We know that each s subshell can hold maximum 2 electrons, each p subshell can hold maximum 6 electrons, each d subshell can hold maximum 10 electrons, and each f subshell can hold maximum 14 electrons.Īlso, we have to make sure that the electron configuration will match the order of aufbau principle (i.e., the 1s subshell is filled first and then 2s, 2p, 3s… and so on). The 1 st electron shell contains 1s subshell, the 2 nd electron shell contains 2s and 2p subshells, the 3 rd electron shell contains 3s, 3p, and 3d subshells, the 4 th electron shell contains 4s, 4p, and 4d subshells, and the 5 th electron shell contains 5s subshell. Similarly, 2 represents the 2 nd electron shell, 3 represents the 3 rd electron shell, 4 represents the 4 th electron shell, and 5 represents the 5 th electron shell. It is obtained chiefly from the mineral cassiterite, which contains tin dioxide. Tin or also called as Stannum in Latin with the atomic number 50 belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Where, azimuthal quantum number of the subshell. Calculate the maximum number of electrons each subshell can hold using the formula: 4 + 2. Eight of these oddities are Au (gold), Ag (silver), Cu (copper), FE (iron), SN (tin), Pb (lead), Sb (antimony), and Hg (mercury): All were among the elements recognized by the ancient Greeks and Romans, and the abbreviations for those are based on a Latin or Greek term for the element. Tin is the p-block element and it belongs to carbon group. Second, make a table of subshell and its maximum electrons. Tin in Periodic table Tin element is in group 14 and period 5 of the Periodic table. Tin is a post-transition metal in group 14 of the periodic table. Since the atomic number of tin is 50, the total electrons of tin are 50. What is Tin (Sn element) Tin or also called as Stannum in Latin with the atomic number 50 belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Wi… Metal, A material, in chemistry, is called a metal based on the way it reacts to other elements.In the above image, 1 represents the 1 st electron shell. Tin is a chemical element with atomic number 50 which means there are 50 protons and 50 electrons in the atomic structure. Interactive periodic table with up-to-date element property data collected from authoritative sources. Carbon forms more compounds than all the other elements together. about… Periodic Table Of The Elements Carbon, carbon (symbol C) Common, nonmetallic element of group IV of the periodic table. First isolated in 1828 by German chemist Friedrich Wöhler, it is… Periodic Table Of The Elements Chromium, chromium (krō´mēəm), metallic chemical element symbol Cr at.
It ignites spontaneously in air and can be l… Periodic Table of the Elements Polonium, polonium (symbol Po) Rare radioactive metallic element of group VI of the periodic table, discovered in 1898 by Polish-born French scientist Marie Cu… Periodic Table Of The Elements Yttrium, yttrium (symbol Y) Silver-grey, metallic element in group III of the periodic table.
Periodic Table of the Elements Rubidium, rubidium (symbol Rb) Silver-white metallic element of the alkali metals (group I of the periodic table).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
